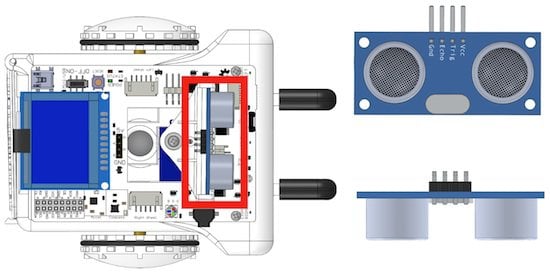
Sparki has an Ultrasonic Range Finder that measures distance with sound waves like a wireless sonic ruler.
How It Works
This sensor finds objects with sound the same way a bat or dolphin does. One part of the sensor is a speaker that sends out a sound wave. The other part is a microphone that then measures how long it takes for the sound wave to come back. The longer it takes to come back, the further away the object:
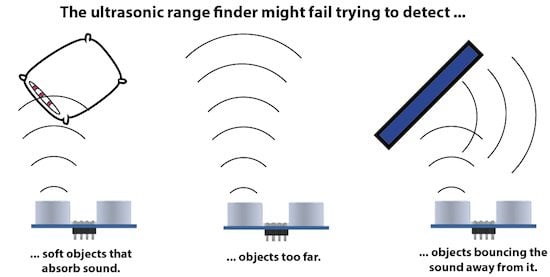
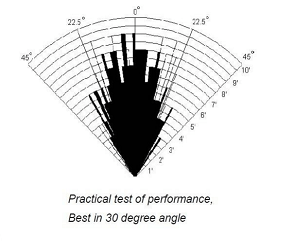
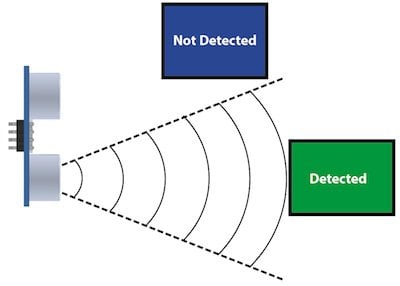
Measure the time it takes for the sound to come back, and you can tell the distance. The speaker sends out the sound in a cone, so only objects within the cone will return sound and be detected. Objects in the center of the cone do best.
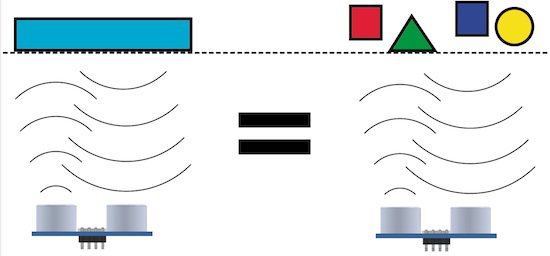
This sensor is a simple ultrasonic rangefinder. It cannot detect individual objects. It can only tell you how long it took the sound sent out to return. It will measure the closest object.
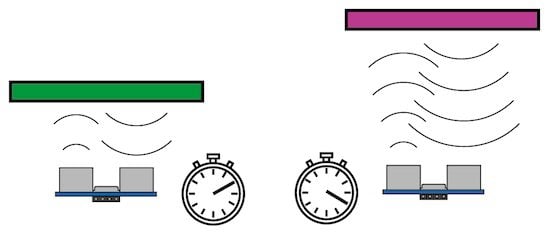
If the object absorbs sound, or if there is nothing for a long distance, or if the object bounces the sound at an angle, there might not be enough sound returning to measure anything.
Using the Sensor
With the basic Sparki code in place, you can measure an infrared sensor by using this command:
sparki.ping();
This command returns the distance the sensor reads in centimeters in the form of a float.
SparkiDuino already has code examples for you to use:
File > Examples->Ultrasonic_Range_Finder
/*******************************************
Basic Ultrasonic test
Show the distance Sparki's eyes are reading
on the LCD. Sparki will beep when something
is too close. If it measures -1, that means
the sensor is either too close or too far
from an object
********************************************/
#include <Sparki.h> // include the robot library
void setup()
{
}
void loop()
{
sparki.clearLCD();
int cm = sparki.ping(); // measures the distance with Sparki's eyes
sparki.print("Distance: ");
sparki.print(cm); // tells the distance to the computer
sparki.println(" cm");
if(cm != -1) // make sure its not too close or too far
{
if(cm < 10) // if the distance measured is less than 10 centimeters
{
sparki.beep(); // beep!
}
}
sparki.updateLCD();
delay(100); // wait 0.1 seconds (100 milliseconds)
}
Advanced Information
Operations
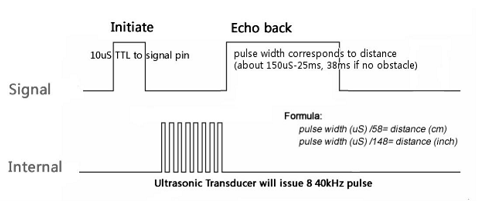
A 10uS high pulse on the Trigger pin initiates an 8 cycle burst of 40khz ultrasonic pulses. The pulses return to the module, and it emits on the Echo pin a high pulse between 150uS and 25ms. The distance can be calculated from the formulas above. They are derived from:
Test distance = (high level time * velocity of sound (340M/S) / 2.
Specifications
- Working Voltage: DC 5 V
- Working Current: 15mA
- Working Frequency: 40Hz
- Max Range: 4m
- Min Range: 2cm
- Measuring Angle: 15 degree
- Trigger Input Signal 10uS TTL pulse
- Echo Output Signal Input TTL lever signal and the range in proportion
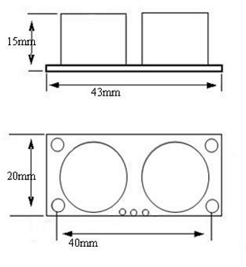
- Dimensions: 45*20*15mm